Lets Go Learning About Questioners With me
Heloo guys ,this time I will explain about questionnaire, want to know ??
See my explanation !
1. Definition of Questioner
• The Questionnaire/Questionnaire is a well-formulated list of questions used as a means of collecting data through surveys.
• A questioner is someone who asks questions, especially in an official or formal capacity. When a detective interviews a suspect, she acts as a questioner.
2. Function of Questioner
The functions of the questionnaire include,
• In order to collect information as a basis for the preparation of permanent records.
• In order to ensure the validity of the information obtained by other methods.
• Making an evaluation of the guidance program.
• In order to take a sampling of attitudes or opinions of respondents.
3. Sample of Questioner
Source : https://images.app.goo.gl/3MZqJvz6Aw7wUvPG8
• The picture above is an example of a research questionnaire about client questionnaire Which contains the services of a company
4. Expressions and sentences used in Questioner
a) What (Apa)
What is used to ask for information about something.
Example of sentences:
• What is your name? (Siapa namamu?)
• What are you doing? (Apa yang kamu lakukan?)
• What is the color? (Apa warnanya?)
• What should I do? (Apa yang harus aku lakukan?)
b) Where (di mana)
Where is used to ask for a location or place.
Example of sentences:
• Where is your Mum? (Di mana ibumu?)
• Where is my shoes? (Di mana sepatumu?)
• Where are you? (Di mana kamu?)
• Where is your house? (Di mana rumahmu?)
c) When (kapan)
When is used to ask for the time.
Example of sentences:
• When does the bus arrive? (Kapan bisnya sampai?)
• When will you be here? (Kapan kamu akan datang kemari?)
• When will the football game start? (Kapan pertandingan sepak bolanya dimulai?)
• When are we going? (Kapan kita akan pergi?)
d) Why (kenapa)
• Why is used to ask a reason.
• Example of sentences:
• Why do you do that? (Kenapa kamu melakukannya?)
• Why do you like Nasi Goreng so much? (Kenapa kamu sangat suka Nasi Goreng?)
• Why the living room is so messy? (Kenapa ruang tamu sangat berantakan?)
• Why the price is expensive? (Kenapa harganya sangat mahal?)
e) Which (yang mana)
Which is used to inquire from the certainty of a choice among people, things, or things.
Example of sentences:
• Which cake is the most delicious? (Kue mana yang lebih enak?)
• Which dress is better for me? (Gaun yang mana yang lebih baik untukku?)
• Which club do you join in? (Di klub mana kamu bergabung?)
• Which cat is yours? (Kucing mana yang jadi milikmu?)
f) Who (siapa)
• Who is used to ask about people.
• Example of sentences:
• Who ate my pudding? (Siapa yang memakan pudingku?)
• Who is your favourite artist? (Siapa artis kesukaanmu?)
• Who are you? (Siapa kamu?)
• Who sent me this gift? (Siapa yang mengirim hadiah ini?)
g) Whom (dengan siapa)
Whom is used to ask someone who has a position as an object or recipient of the subject's action.
Example of sentences:
• Whom did he marry? (Dengan siapa dia menikah?)
• Whom did you talk to? (Dengan siapa kamu bicara?)
• Whom you do you know in USA? (Ada yang kamu kenal di AS?)
• Whom did you see? (Siapa yang kamu lihat/temui?)
• Whom did she make a pie for? (Siapa yang kamu buatkan pai?)
h) Whose (punya siapa)
Whose is used to ask which person has something (possessive).
Example of sentences:
• Whose child is this? (Anak siapa ini?)
• Whose turn is this? (Giliran siapa ini?)
• Whose car is that? (Mobil (milik) siapa itu?)
• Whose house is this? (Rumah (milik) siapa ini?)
i) How (bagaimana)
How is used to ask how something can be done.
Example of sentences:
• How are you? (Bagaimana kabarmu?)
• How to make this cake? (Bagaimana cara membuat kue ini?)
• How can I go home right now? (Bagaimana caraku pulang ke rumah sekarang?)
• How does the television work? (Bagaimana cara televisi bekerja?)
5. Types of Questioners
The following is about the Types of Questions and Sample Questions:
a. Open Questions
This open-ended question cannot be answered with a "Yes" or "No" answer. The purpose of open-ended questions is to encourage the answerer to develop an answer to the question. Open-ended questions begin with the words "Why", "Who", "When", "What", "Where”.
Example of an open question:
Why do you like golf?
When do you play golf?
b. Closed Questions
Closed questions are answered with the answers "Yes", "No", "Agree", "Disagree, "True" "False".
Example of a closed question:
Lawyer is a profession in the field of law, True or False.
c. Specific Questions
These specific questions are questions that ask for specific information.
Examples of specific questions:
At what time do you feel bored playing golf?
d. Reflective Questions
This reflective question aims to provide more in-depth information.
Examples of reflective questions:
It turns out that Lawyer is a profession that...?
e. Leading Questions
This directing question aims to make it easier for the answerer and the answer to the question is already in the question submitted.
Example of a leading question:
It turns out that the Lawyer profession is very fun, isn't it?
f. Hypothesis Questions
Hypothesis questions aim to find out reactions and speed of thinking in solving problems.
Example of a hypothetical question:
As a lawyer what do you do if you lose the trial?
g. Behaviour Questions
Behavioural questions are questions that ask about experience or what the answerer does.
Examples of behavioural questions:
Try to explain what you do as a lawyer in defending clients in court.
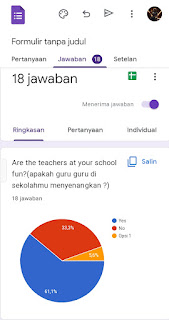
6. Doing Questioners
I made this questioners about a teacher
From the results above I can find out what teacher my friend likes,and some people likes Mr. Yoga and others like different teacher.









Komentar
Posting Komentar